
![]()
 |
 |
||
 |
GIF | ||
|
|
|||
| Go to: -Introduction |
Introduction: Semi-Analytic Galaxy Formation - GIF The simulations in this section explicitly include processes related
to the formation and evolution of galaxies. In particular, they include
detailed phenomenological modelling of gas cooling, of star formation,
of stellar population evolution, of feedback from massive stars and supernovae,
and of galaxy merging using recipes outlined in Kauffmann et al (1999).
In some cases, chemical evolution of the interstellar medium of galaxies
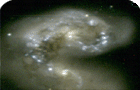
and of the hot intergalactic medium is also included. Scientists involved in the GIF project combined the large high-resolution N-body simulations with semi-analytical models to study formation and evolution of galaxies. The picture below, created by Joerg Colberg and Antonaldo Diaferio, shows the population of galaxies superposed on dark-matter distribution (grey-colored) in a small region of 21x21x8 (Mpc/h)3. (See also the picture of dark-matter distribution below.) Galaxies are shown as circles colour-coded according to their star formation rate: the sequence red, yellow, green and blue represents an increasing rate of star formation. At early times (top left panel) there exist only a few galaxies forming stars at a very high rate. As time goes on, from z=3 to z=0, more galaxies form and, at the same time, some galaxies run out of gas, form fewer stars and become green, yellow and red. At the present time (z=0), red galaxies populate the central region of the cluster, whereas blue galaxies can be found in the outskirts of the system. This is very similar to what is observed in the real Universe. Galaxy population in GIF simulations different formats: Credit: Joerg Colberg and Antonaldo Diaferio
For all of the following images the credit should be given to Kauffmann, Colberg, Diaferio, and White, see references. Pic.1 Projected dark matter distribution at z=3, 2, 1, and 0 (tauCDM) larger versions:
Pic.2 Dark Matter at z=0 plus model galaxies formed at different
epoch (tauCDM). larger formats:
Pic.3 Dark Matter plus model galaxies at z=3, 2, 1, and 0 (tauCDM) larger versions:
Pic.4 Dark Matter distribution of GIF boxes of four different
cosmologies. larger versions:
Pic.5 A slice of thickness 8 Mpc/h through the whole simulation box (which is 85 Mpc/h on a side) would look like this. The colours now denote the B-V colours of the galaxies, ranging from red for ellipticals to blue for irregulars. larger versions:
Pic.6 One of the clusters from the tauCDM simulation at z=0. larger versions:
Galaxy catalogues and dark halo catalogues for the LCDM model are available!
The Large-scale Distribution of Galaxies, G. Kauffmann,A. Diaferio, Annual Report of the MPA, 1998, pp.25-29
The Spatial and Kinematic Distributions of Cluster Galaxies in
a LCDM Universe - Comparison with Observations, A. Diaferio, G.
Kauffmann, M. L. Balogh, S.D.M. White, D. Schade and E. Ellingson MNRAS,
in press,
Comments to: H. Mathis |