|
|  |
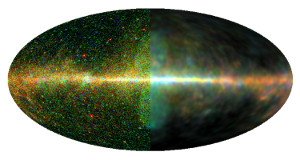
The sky in the light of gamma-radiation shows a variety of objects, structures,
and astrophysical processes (Fig. 1). It is most prominently illuminated by the
Milky Way, which contributes a great part of the point sources as well as the
major part of the diffuse gamma-radiation in the sky. The various radiation
sources appear superimposed, which complicates their identification and
interpretation. Furthermore, our measurement instruments, such as the Fermi
satellite, record only individual gamma photons, arriving at random times from
random directions. These are highly energetic light particles, whose
observation requires complex imaging algorithms in order to reconstruct sky
maps. A new method for denoising, deconvolving, and decomposing photon
observations, called
 D3PO, developed at the Max Planck
Institute for Astrophysics, has now created the by far most brilliant
gamma-radiation map of the sky from the data of the Fermi satellite (Fig. 1). D3PO, developed at the Max Planck
Institute for Astrophysics, has now created the by far most brilliant
gamma-radiation map of the sky from the data of the Fermi satellite (Fig. 1).
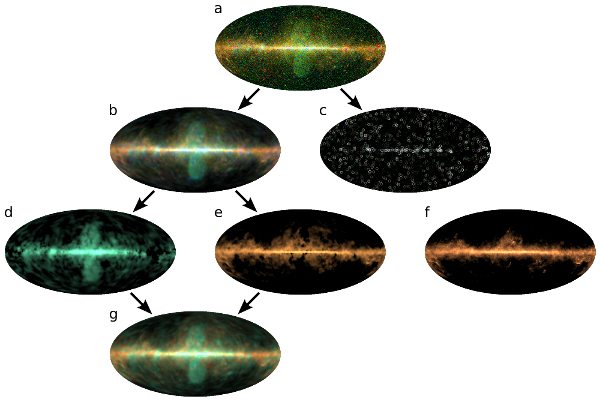
D3PO has decomposed the gamma-ray sky into point sources (Fig. 2c)
and diffuse radiation at nine photon energies. From these, a colored image can
be generated (Fig. 2b), which shows the diffuse sky as it would appear to an
observer with gamma-eyes. The different astrophysical processes can be
recognized therein via their different energy spectra, visible as different
colors (Fig. 2b). The gamma-bubbles above (and below) the center of the Milky
Way appear blue-greenish, which indicates particularly high-energy
gamma-radiation. This should have been mainly generated by collisions of
electrons that are moving almost with the speed of light with starlight and
other photons. The orange-brown areas on the right and left side are primarily
caused by collisions of super-fast protons with nuclei in dense, cold gas
clouds.
The big surprise was that the central bright Galactic disk, and virtually all
other areas of the sky, show essentially just a superposition of these two
processes: collisions of protons with nuclei and of electrons with photons. If
we decompose the diffuse gamma-radiation into only these two processes (Fig. 2d
and 2e), more than 90% of the radiation is explained – and this at all studied
sky locations and energies (Fig. 2g). The total diffuse galactic
gamma-radiation is thus produced almost exclusively by two typical media:
dense, cold gas clouds and the thin, hot gas between them. In fact,
gamma-radiation coming from the clouds shows almost the same spatial
distribution as the Galactic dust clouds as measured by the Planck satellite in
the microwave range (Fig. 2f).
The gamma-radiation generated by electrons in the mysterious gamma-ray bubbles
does not differ in color from the electron-generated radiation from the
Galactic disk. This suggests that we see the same material in both places: hot
gas that has been enriched with electrons moving almost at the speed of light
by supernova explosions. The gamma-bubbles are therefore simply rising hot gas
masses, leaving the center of our Milky Way.
In addition to unraveling the gamma-ray bubbles, the D3PO analysis
of the anatomy of Galactic gamma-radiation has delivered a number of other
scientific results. It was shown that the cold gas clouds that are illuminated
by the gamma-radiation extend up to larger heights above the Galactic plane
than the dust clouds measured by the Planck satellite. While this could have
been expected due to the higher mass of dust particles in comparison with the
gas particles, it is a nice confirmation of the astrophysical correctness of
these anatomical dissections of the Galaxy in gamma light. Furthermore, a
comprehensive catalog of point sources was generated and searched for
gamma-radiation from clusters of galaxies – unfortunately without success.
The D³PO algorithm that has made all this possible is now
 freely available
and will in the future also provide astronomical images at other wavelengths of
light. D³PO was developed by Marco Selig during his just-completed doctorate
with honors at the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (Fig. 3). The
algorithm was derived within freely available
and will in the future also provide astronomical images at other wavelengths of
light. D³PO was developed by Marco Selig during his just-completed doctorate
with honors at the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (Fig. 3). The
algorithm was derived within  information field theory)
and implemented using the also freely available information field theory)
and implemented using the also freely available  NIFTY-software
for numerical information field theory. Information field theory deals with the
mathematics of imaging complex data sets and is a central focus of the research
group of Torsten Ensslin at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics. NIFTY-software
for numerical information field theory. Information field theory deals with the
mathematics of imaging complex data sets and is a central focus of the research
group of Torsten Ensslin at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics.
Marco Selig, Valentina Vacca, Niels Oppermann, Torsten Enßlin.
References:
Publication: The Denoised, Deconvolved, and Decomposed Fermi γ-ray Sky - An
Application of the D3PO Algorithm. Marco Selig, Valentina Vacca, Niels
Oppermann, Torsten A. Enßlin
submitted to Astronomy & Astrophysics,  preprint: arXiv:1410.4562, preprint: arXiv:1410.4562,  Bild & Daten Bild & Daten
Instruments:  Fermi satellite and its Fermi satellite and its
 gamma-ray data
& gamma-ray data
&  Planck satellite
and its Planck satellite
and its  dust emission map dust emission map
D3PO:  Description & Description &  software software
NIFTY:  Description
& Description
&  software software
 Information field theory Information field theory
|